 Short Bytes: Here
are the simple and easy steps on how to find, kill and delete a remote
connecting malware using command prompt on Windows 10. These steps
use PID of an unwanted remote connection and based on that, we take the
further actions to delete the malware.
Short Bytes: Here
are the simple and easy steps on how to find, kill and delete a remote
connecting malware using command prompt on Windows 10. These steps
use PID of an unwanted remote connection and based on that, we take the
further actions to delete the malware.
Command
prompt can be a useful tool in scanning virus and malware that are
running in the background, trying to establish a remote connection from
our personal computers.We have already covered a topic regarding tips to remove virus from USB or any drive using CMD, and now is the time to uncover malware which runs in the background.
So,
when a malware is running in the background, it must establish a
connection to the outside internet world. They also use a protocol like
TCP or UDP to establish the internet connection and send our private
information outside. Another important factor is that every process is
assigned a PID (Process ID) in Windows.
So, using the simple cmd commands, we will try to extract all these information and then kill the unwanted process (suspected malware) based on its PID.

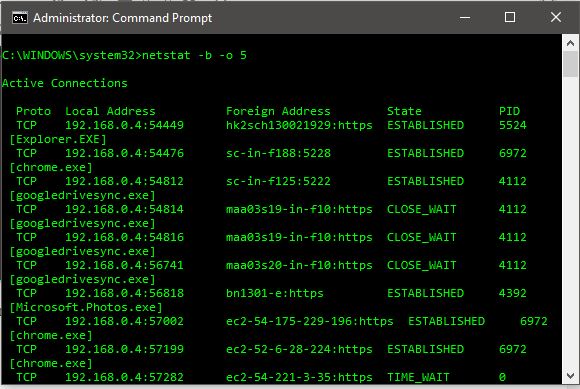
Some of the active connections in the above screenshots are googledrivesync.exe, explorer.exe, chrome.exe and I do not see any suspicious connection like autorun.exe or autorun.inf. So, once you find these suspected executable active connections, note their PID.
So, we can print the output of the netstat -b -o 5 command to a text file using the below command and analyze that output file.
Forget not to check this file as soon as possible because PID of the process may change over the time as well.
So, using the simple cmd commands, we will try to extract all these information and then kill the unwanted process (suspected malware) based on its PID.
Find And Kill Remote Connecting Malware On Windows 10:
Please follow the steps mentioned below:- Run Command Prompt as administrator.

- Type netstat -b -o 5 in your Command Prompt screen

- Here is what we are trying to do with the above command:
- netstat: The netstat is a useful command for checking internet and network connections.
- -b attribute: displays the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port.
- -o attribute: displays the owning process id associated with each connection.
- integer: An integer used to display results multiple times with specified number of seconds between displays. It continues until stopped by command ctrl+c.
Some of the active connections in the above screenshots are googledrivesync.exe, explorer.exe, chrome.exe and I do not see any suspicious connection like autorun.exe or autorun.inf. So, once you find these suspected executable active connections, note their PID.
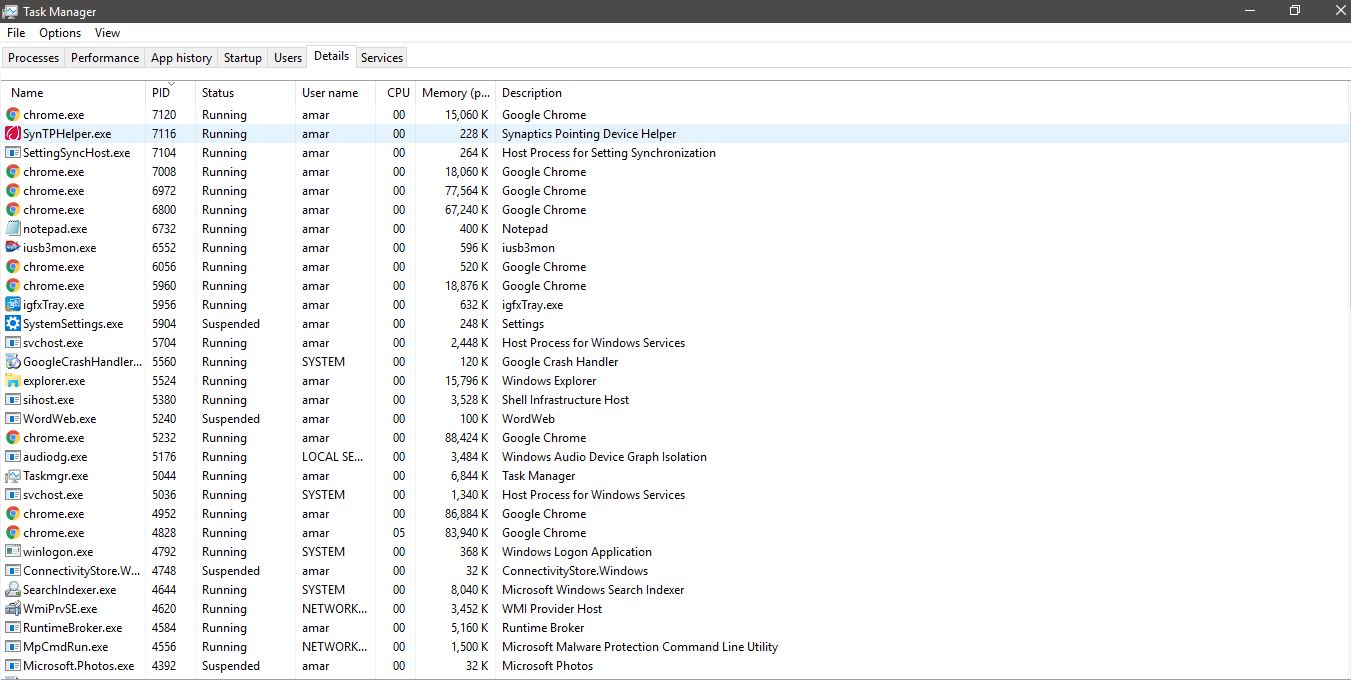
- Now open your Task manager and go to the ‘Details’ tab. Under the details tab, you can see the name, PID, status and some more information about the running applications.

- You can also sort the PID by clicking on this tab at the top. Once the Process IDs are sorted out, you can find the suspected PID here.
- Right click on that particular PID and you can see many options out of which two important options for you are:
- End task
- Open file location
- Do no click on ‘End task’ before opening the file location. So, first click on the ‘open file location’ which will open the location of the suspected malware and then you can end that task.
- In the file location, you can delete the malware. If you are unable to delete the malware, you can follow our article — Remove Virus from USB Or Any Drive on Windows 10 Using CMD.
So, we can print the output of the netstat -b -o 5 command to a text file using the below command and analyze that output file.
- netstat -b -o 5>>sus-mal.txt
Forget not to check this file as soon as possible because PID of the process may change over the time as well.



 5/08/2016 01:47:00 PM
5/08/2016 01:47:00 PM
 Unknown
Unknown



1 comments:
Using AVG security for a few years now, I'd recommend this solution to all of you.
Post a Comment